共计 7554 个字符,预计需要花费 19 分钟才能阅读完成。
一般使用的 万年历,只提供距今前后百年的日历。这是因为其所用的计算方法是一种简便的近似计算,适用范围较小。其次,天文学方法计算量大,不适合日常软件使用。但如果要进行历史研究,范围就超出常用日历,本文即实现计算任意日期的农历。
由于天文星历数据太大,本文的代码是直接利用 python 的 PyEphem 库。该库只提供了二分二至时间,没有 24 节气。但是也提供了任意时间的太阳黄经,可以利用此项计算 24 节气。
本文提供三个功能:PerpetualCalendar 万年历,Solar2LunarCalendar 公历转农历,Lunar2SolarCalendar 农历转公历
中国阴阳历基础:
-
以太阳历确定岁首,方法是通过测量影长确定冬至。以冬至所在月为子月,其后每月依次排序,闰月无建。
-
现行农历用寅正,即冬至后第二个月(冬至月起的第三月),冬至固定在十一月。
-
将二十四节气中的偶数序的节气称为十二中气。每月对应一个中气,若无中气,则该月作为闰月。
-
同时定气和定朔的情况下,可能出现多个无中气月,如此则规定只有连续两个冬至月之间出现十三次合朔年份的的第一个无中气月置闰。
-
使用节气月排定月份干支。
详细农历分析另见 农历计算方法 一文。
本文提供的简易万年历直接控制台打印:
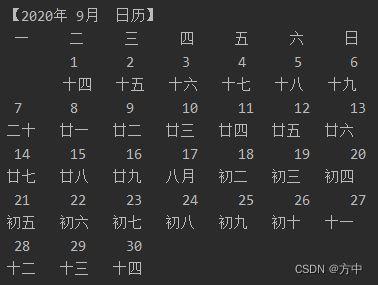
如需下图所示 UI 程序,另见:Python 万年历(含农历、节气等)
import math, ephem
lunar_months =["正月","二月","三月","四月","五月","六月","七月","八月","九月","十月","十一月","十二月"]
lunar_dates = ["初一","初二","初三","初四","初五","初六","初七","初八","初九","初十","十一","十二","十三","十四","十五","十六","十七","十八","十九","二十","廿一","廿二","廿三","廿四","廿五","廿六","廿七","廿八","廿九","三十"]
heavenly_stems = ["甲","乙","丙","丁","戊","己","庚","辛","壬","癸"]
earthly_branches = ["子","丑","寅","卯","辰","巳","午","未","申","酉","戌","亥"]
gz = [''] * 60 # 六十甲子表
for i in range(60):
gz[i] = heavenly_stems[i % 10] + earthly_branches[i % 12]
def JD2date(JD, ut=0):
return ephem.Date(JD + ut/24 - 2415020)
def EquinoxSolsticeJD(year, angle):
if 0 <= angle < 90:
date = ephem.next_vernal_equinox(year)
elif 90 <= angle < 180:
date = ephem.next_summer_solstice(year)
elif 180 <= angle < 270:
date = ephem.next_autumn_equinox(year)
else:
date = ephem.next_winter_solstice(year)
JD = ephem.julian_date(date)
return JD
# 计算二十四节气
def SolarLongitube(JD):
date = JD2date(JD)
s = ephem.Sun(date) # date 应为 UT 时间
sa = ephem.Equatorial(s.ra, s.dec, epoch=date)
se = ephem.Ecliptic(sa)
L = se.lon / ephem.degree / 180 * math.pi
return L
def SolarTerms(year, angle):
if angle > 270: year -= 1 # 岁首冬至
if year == 0: year -= 1 # 公元 0 改为公元前 1
JD = EquinoxSolsticeJD(str(year), angle) # 初值
if angle >= 270:
JD0 = EquinoxSolsticeJD(str(year), (angle - 90) % 360)
if JD < JD0: # 非年末冬至
JD = EquinoxSolsticeJD(str(year+1), angle) # 转入次年
JD1 = JD
while True:
JD2 = JD1
L = SolarLongitube(JD2)
JD1 += math.sin(angle * math.pi / 180 - L) / math.pi * 180
if abs(JD1 - JD2) < 0.00001:
break # 精度小于 1 second
return JD1 # UT
def DateDiffer(JD1, JD2):
return math.floor(JD1 + 8 / 24 + 0.5) - math.floor(JD2 + 8 / 24 + 0.5)
def DateCompare(JD1, JD2): # 输入 ut,返回 ut+8 的比较结果
if DateDiffer(JD1, JD2) >= 0: return True # JD1 >= JD 2
else: return False
def findSZY(JD, shuoJD): # 查找 JD 所在的农历月份
szy = -1
for i in range(len(shuoJD)):
if DateCompare(JD, shuoJD[i]):
szy += 1 # date 所在的阴历月序,起冬至朔
return szy
def findDZS(year): # 寻找年前冬至月朔日
if year == 1: year -= 1 # 公元元年前冬至在公元前 1 年
dz = ephem.next_solstice((year - 1, 12)) # 年前冬至
jd = ephem.julian_date(dz)
# 可能的三种朔日
date1 = ephem.next_new_moon(JD2date(jd - 0))
jd1 = ephem.julian_date(date1)
date2 = ephem.next_new_moon(JD2date(jd - 29))
jd2 = ephem.julian_date(date2)
date3 = ephem.next_new_moon(JD2date(jd - 31))
jd3 = ephem.julian_date(date3)
if DateCompare(jd, jd1): # 冬至合朔在同一日或下月
return date1
elif DateCompare(jd, jd2) and (not DateCompare(jd, jd1)):
return date2
elif DateCompare(jd, jd3): # 冬至在上月
return date3
def LunarCalendar(nian, type=1): # type=1 时截止到次年冬至朔,=0 时截止到次年冬至朔次月
dzs = findDZS(nian)
shuo = dzs # 计算用朔,date 格式
shuoJD = [ephem.julian_date(dzs)] # 存储 ut+8 JD,起冬至朔
next_dzsJD = ephem.julian_date(findDZS(nian + 1)) # 次年冬至朔
i = -1 # 中气序,从 0 起计
j = -1 # 计算连续两个冬至月中的合朔次数,从 0 起计
zry = 0
flag = False
# 查找所在月及判断置闰
while not DateCompare(shuoJD[j+type], next_dzsJD): # 从冬至月起查找,截止到次年冬至朔
i += 1
j += 1
shuo = ephem.next_new_moon(shuo) # 次月朔
shuoJD.append(ephem.julian_date(shuo))
# 查找本月中气,若无则置闰
if j == 0: continue # 冬至月一定含中气,从次月开始查找
angle = (-90 + 30 * i) % 360 # 本月应含中气,起冬至
qJD = SolarTerms(nian, angle)
# 不判断气在上月而后气在后月的情况,该月起的合朔次数不超过气数,可省去
if DateCompare(qJD, shuoJD[j+1]) and flag == False: # 中气在次月,则本月无中气
zry = j + 1 # 置闰月
i -= 1
flag = True # 仅第一个无中气月置闰
# 生成农历月序表
ymb = []
for k in range(len(shuoJD)):
ymb.append(lunar_months[(k - 2) % 12]) # 默认月序
if j + type == 13: # 仅 12 次合朔不闰,有闰时修改月名
if k + 1 == zry:
ymb[k] = '闰' + lunar_months[(k-1 - 2) % 12]
elif k + 1 > zry:
ymb[k] = lunar_months[(k-1 - 2) % 12]
return ymb, shuoJD # 月名表,合朔 JD 日期表
def PerpetualCalendar(year, lunar_months=0): # 万年历(农历及公历对照),不指定月份时输出全年
if year == 0: return print('不存在公元 0 年')
ymb, shuoJD = LunarCalendar(year, 0)
if DateCompare(ephem.julian_date((year, 12, 31)), shuoJD[-2] + 29):
ymb1, shuoJD1 = LunarCalendar(year+1)
ymb = ymb[:-2] + ymb1[:2]
shuoJD = shuoJD[:-2] + shuoJD1[:3]
days = [31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31]
days[1] = 29 if (year % 4 == 0 and year % 100 != 0) or year % 400 == 0 else 28
if year < 1582 and year % 4 == 0: days[1] = 29
week = ['一', '二', '三', '四', '五', '六', '日', ]
for j in range(12):
if lunar_months != 0 and j + 1 != lunar_months: continue
print('【' + str(year) + '年 ' + str(j+1) + '月 日历】')
ysJD = ephem.julian_date((year, j+1))
szy = findSZY(ysJD, shuoJD) # 公历岁首对应的农历月
ysRQ = DateDiffer(ysJD, shuoJD[szy]) # 每月 1 日的农历日期
yue0 = DateDiffer(shuoJD[szy + 1], shuoJD[szy])
yue1 = DateDiffer(shuoJD[szy + 2], shuoJD[szy + 1])
blank = int((ysJD + 0.5) % 7)
flag = False
for row in range(6*2+1):
if row % 2 == 1 and flag: break
for k in range(7):
if row % 2 == 1: # 公历行
day = row // 2 * 7 + k - blank + 1
if year == 1582 and j == 9:
if day > 4: day += 10
elif row != 0: # 农历行
if row == 2 and k >= blank or row > 2:
rqx = ysRQ + row // 2 * 7 - 7 + k - blank
if rqx == 0: rq = ymb[szy]
elif 0 < rqx < yue0: rq = lunar_dates[rqx]
elif rqx == yue0: rq = ymb[szy+1]
elif yue0 < rqx < yue0 + yue1: rq = lunar_dates[rqx - yue0]
elif rqx == yue0 + yue1: rq = ymb[szy + 2]
elif rqx > yue0 + yue1: rq = lunar_dates[rqx - yue0 - yue1]
# 输出排版
if row == 0: print(" {:<5}".format(week[k]), end='')
elif row == 1 or row == 2: # 首行
if k == 0:
print(' ' * blank, end='')
if row == 1 and k >= blank:
print(" {:<6d}".format(day), end='')
if row == 2 and k >= blank:
print("{0:{1}<3}".format(rq, '\u3000'), end=' ')
else:
if row % 2 == 1 and row != 1:
if day <= days[j]:
print(" {:<6d}".format(day), end='')
else:
flag = True
break
if row % 2 == 0 and row != 0 and row != 2:
if year == 1582 and j == 9 and day > days[j]: break
print("{0:{1}<3}".format(rq, '\u3000'), end=' ')
if row // 2 * 7 + k - blank - 6 >= days[j]: break
print()
print()
def Solar2LunarCalendar(date): # 默认输入 ut+8 时间
if date[0] == '0': return '不存在公元 0 年'
JD = ephem.julian_date(date) - 8/24 # ut
year, lunar_months, day = JD2date(JD, 8).triple()
# 判断所在年
dzs = findDZS(year) # 本年冬至朔
next_dzs = findDZS(year+1) # 次年冬至朔
this_dzsJD = ephem.julian_date(dzs)
next_dzsJD = ephem.julian_date(next_dzs)
nian = year # 农历年
if DateCompare(JD, next_dzsJD): # 该日在次年
nian += 1
if not DateCompare(JD, this_dzsJD): # 该日在上年
nian -= 1
# 判断所在月
ymb, shuoJD = LunarCalendar(nian)
szy = findSZY(JD, shuoJD)
# 判断节气月
if year < 0: year += 1
jqy, jqr = JD2date(SolarTerms(year, lunar_months*30 + 255), 8).triple()[1:]
if int(jqy) != lunar_months: lunar_months -= (int(jqy) - lunar_months)
if day >= int(jqr): ygz = gz[(year * 12 + 12 + lunar_months) % 60]
else: ygz = gz[(year * 12 + 11 + lunar_months) % 60]
# 以正月开始的年干支
if szy < 3: nian -= 1 # 正月前属上年
if nian < 0: nian += 1
ngz = gz[(nian - 4) % 60]
rgz = gz[math.floor(JD + 8/24 + 0.5 + 49) % 60]
rq = DateDiffer(JD, shuoJD[szy]) # 月内日期
return date + ' 为农历:' + ngz + '年 ' + ygz + '月 ' + rgz + '日 ' + ymb[szy] + lunar_dates[rq] + '\n'
def Lunar2SolarCalendar(nian, date): # 正月开始的年
date1 = date.split('闰')[-1]
year = nian
yx = lunar_months.index(date1[:-2])
if yx + 1 > 10: year += 1 # 计算用年,起冬至朔
if year == 0: return '不存在公元 0 年'
yx = (yx + 2) % 12 # 子正转为寅正
if "闰" in date: yx += 1
# 查找所在月
ymb, shuoJD = LunarCalendar(year, 0)
szy = 0
for i in range(len(ymb)):
if ymb[i] == date1[:-2]: # 按月序查找
if ymb[i + 1] == date[:-2] or '闰' in date:
szy += 1 # 可能为闰月(不闰则计算次月)
break
szy += 1
# 获得农历日期
try:
rq = lunar_dates.index(date[-2:])
except:
rgz = gz.index(date[-2:])
sgz = math.floor(shuoJD[szy] + 8/24 + 0.5 + 49) % 60
rq = (rgz - sgz) % 60
if DateCompare(shuoJD[szy] + rq, shuoJD[szy+1]):
print('该月无' + date[-2:])
else:
print(date[-2:] + '为该月' + lunar_dates[rq] + '日')
date2 = str(JD2date(shuoJD[szy] + rq, 8))[:-9]
return '农历' + str(nian) + '年' + date + ' 为公历:' + date2
# ========= 测试内容 ===========
#PerpetualCalendar(2020)
#date = input('请输入日期:')
date = "2019-3-15"
date1 = "2016-11-29"
date2 = "2033-9-1" # 无中气月,一年仅得 12 月,不闰
date3 = "2033-12-31" # 冬至起的第一个无中气月,闰
date4 = "2034-3-1" # 冬至起的第二个无中气月,不闰
print(Solar2LunarCalendar(date))
print(Lunar2SolarCalendar(-1696, '十一月甲子'))
print(Solar2LunarCalendar('-1695/1/7'))
print(Lunar2SolarCalendar(2020, '正月初一'))
print(Lunar2SolarCalendar(2033, '闰十一月十一'))天文计算中经常简化历表以简便计算,简化会降低计算精度。特别是时间进位可能会差到一天。计算定气定朔,日期越久远误差越大。如-2/12/26 定朔 23:59:38,若误差约 1 分钟,则可能定朔为 12/27 日。不过这种情况很少见。
本程序虽以 ephem 库为例,但在农历算法上使用一般化的方法使其适用于较宽的年限以便适应不同精度的历表要求。实际上,ephem 库计算月亮位置的精度有限,适用年限也不广。在较小应用的范围内,可根据一些天文学特征简化程序。例如,如果上限不超过 BC1100 年,则无需考虑岁差和不同历法对回归年的取值问题,导致冬至计算结果在次年的情况(此后冬至固定在 12 月)。如果下限也不远,则无需考虑地球自转变慢和近点进动,计算节气利用太阳在近日点和远日点 不同的 运动特点,平气法寻找较好的值(如 31)可以保证定气不会超过平气计算结果从而仅需比较一次即可获得真实节气。
本文转载自:Python 公历转换农历及简易万年历
提醒:本文发布于644天前,文中所关联的信息可能已发生改变,请知悉!







