共计 10181 个字符,预计需要花费 26 分钟才能阅读完成。
一、 实例化基本流程
基本流程图如下:
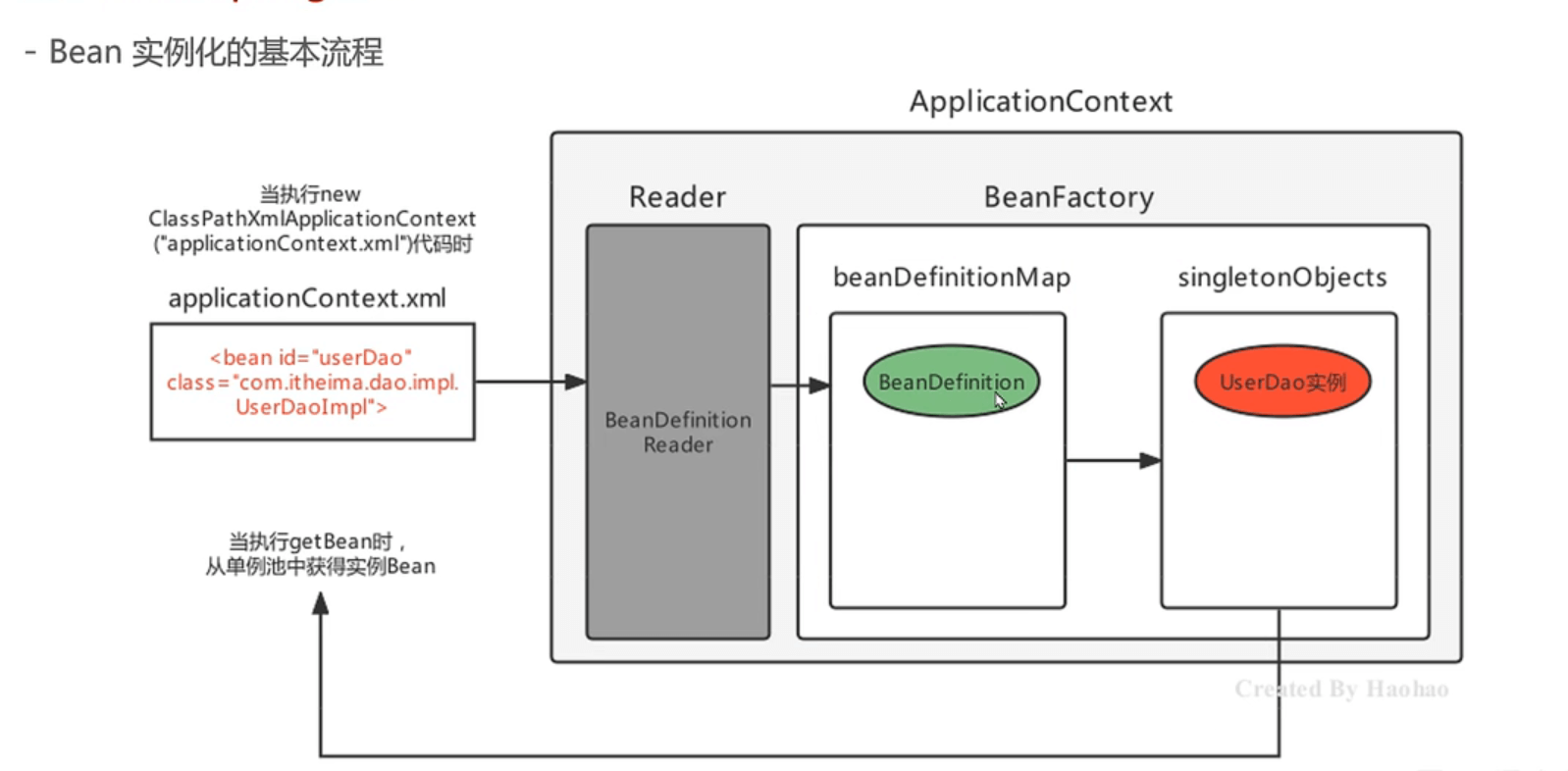
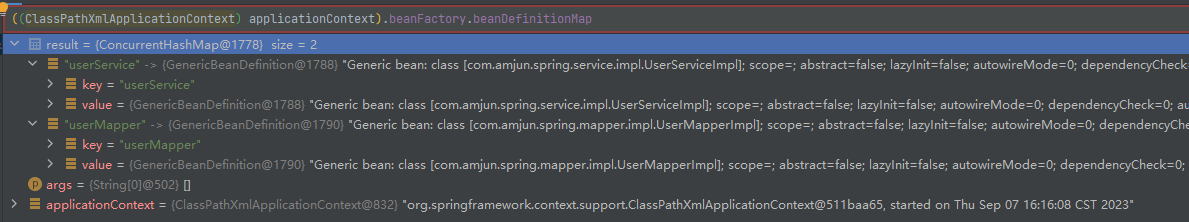
Spring 容器在进行初始化时,会将 xml 配置的 <bean> 的信息封装成一个 BeanDefinition 对象,所有的 BeanDefinition 存储到一个名为 beanDefinitionMap 的 Map 集合中。
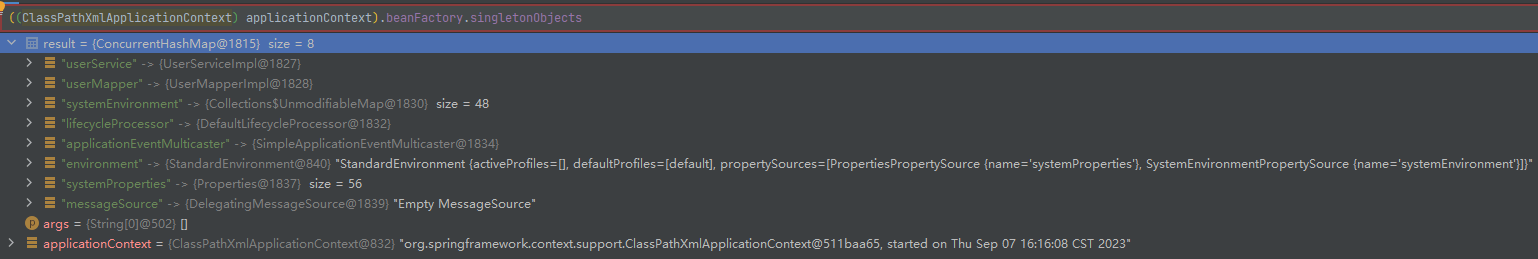
Spring 框架再对该 beanDefinitionMap 进行遍历,使用反射创建 Bean 实例对象,创建好的 Bean 对象存储在一个名为 singletonObjects 的 Map 集合中。
当调用 getBean 方法时则最终从该 singletonObjects 集合中取出 Bean 实例对象返回。
二、 spring后处理器
Spring 的后处理器是 Spring 对外开发的重要扩展点,允许许我们介入到 Bean 的整个实例化流程中来,以达到动态注册 BeanDefinition,动态修改 BeanDefinition,以及动态修改 Bean的作用。Spring 主要有两种后处理器:
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor:Bean工厂后处理器,在 BeanDefinitionMap 填充完毕,Bean 实例化之前执行
- BeanPostProcessor:Bean后处理器,一般在 Bean 实例化之后,填充到单例池 singletonObjects 之前执行。
1 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
1.1 基本使用
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是一个接口规范,实现了该接口的类只要交由 Spring 容器管理的话,那么 Spring 就会回调该接口的方法,用于对 BeanDefinition 注册和修改的功能。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory var1) throws BeansException;
}此时流程图如下:
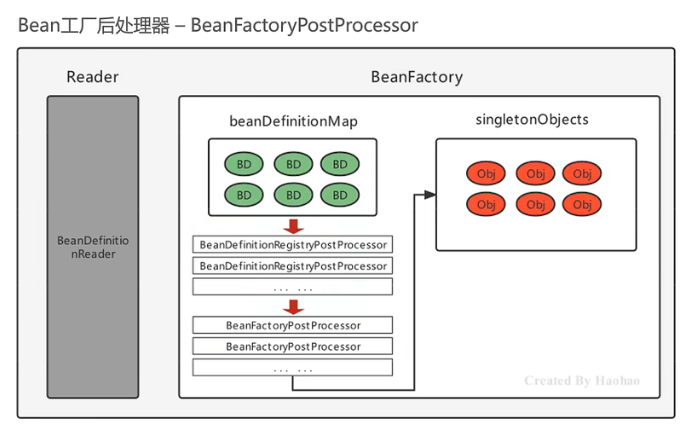
现有如下 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现类:
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.java
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法");
// 修改 BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("userService");
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.amjun.spring.mapper.impl.UserMapperImpl");
// 最好实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口来实现
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
rootBeanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.amjun.spring2.service.impl.PersonServiceImpl");
// beanFactory 实际上是 DefaultListableBeanFactory, 是 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 的子类
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("personService", rootBeanDefinition);
}
}MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor2.java
// 专门用于注册 BeanDefinition
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor2 implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
// 先执行该方法
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor2 的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法");
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
rootBeanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.amjun.spring2.service.impl.PersonServiceImpl");
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("personService2", rootBeanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor2 的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法");
}
}xml 配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.amjun.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
</bean>
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.amjun.spring.mapper.impl.UserMapperImpl">
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.amjun.spring2.processor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor2" class="com.amjun.spring2.processor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor2"></bean>
</beans>测试代码:
public class ApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
/*Object userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);*/
/*Object personService = applicationContext.getBean("personService");
System.out.println(personService);*/
Object personService2 = applicationContext.getBean("personService2");
System.out.println(personService2);
}
}1.2 案例-实现自动扫描

注解类:MyComponent.java
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
String value();
}待扫描的对象 OtherBean.java。
@MyComponent("otherBean")
public class OtherBean {
}MyComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor.java
public class MyComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
// 通过扫描工具去扫描指定包及其子包下的所有类,收集使用@Mycomponent的注解的类
Map<String, Class> stringClassMap = BaseClassScanUtils.scanMyComponentAnnotation("com.amjun.spring2");
// 遍历 Map,组装BeanDefinition进行注册
stringClassMap.forEach((beanName, clazz) -> {
String beanClassName = clazz.getName(); // com.amjun.spring2.beans.OtherBean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName(beanClassName);
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
});
}
}xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.amjun.spring2.processor.MyComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>
</beans>测试方法:
public class ApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
Object otherBean = applicationContext.getBean("otherBean");
System.out.println(otherBean);
}
}2 BeanPostProcessor
Bean 被实例化后,到最终缓存到名为 singletonObjects 单例池之前,中间会经过 Bean 的初始化过程,例如:属性的填充、初始方法 init 的执行等,其中有一个对外进行扩展的点 BeanPostProcessor,我们称为 Bean 后处理。跟上面的 Bean 工厂后处理器相似,它也是一个接口,实现了该接口并被容器管理的 BeanPostProcessor,会在流程节点上被 Spring 自动调用。
此时的流程图如下:
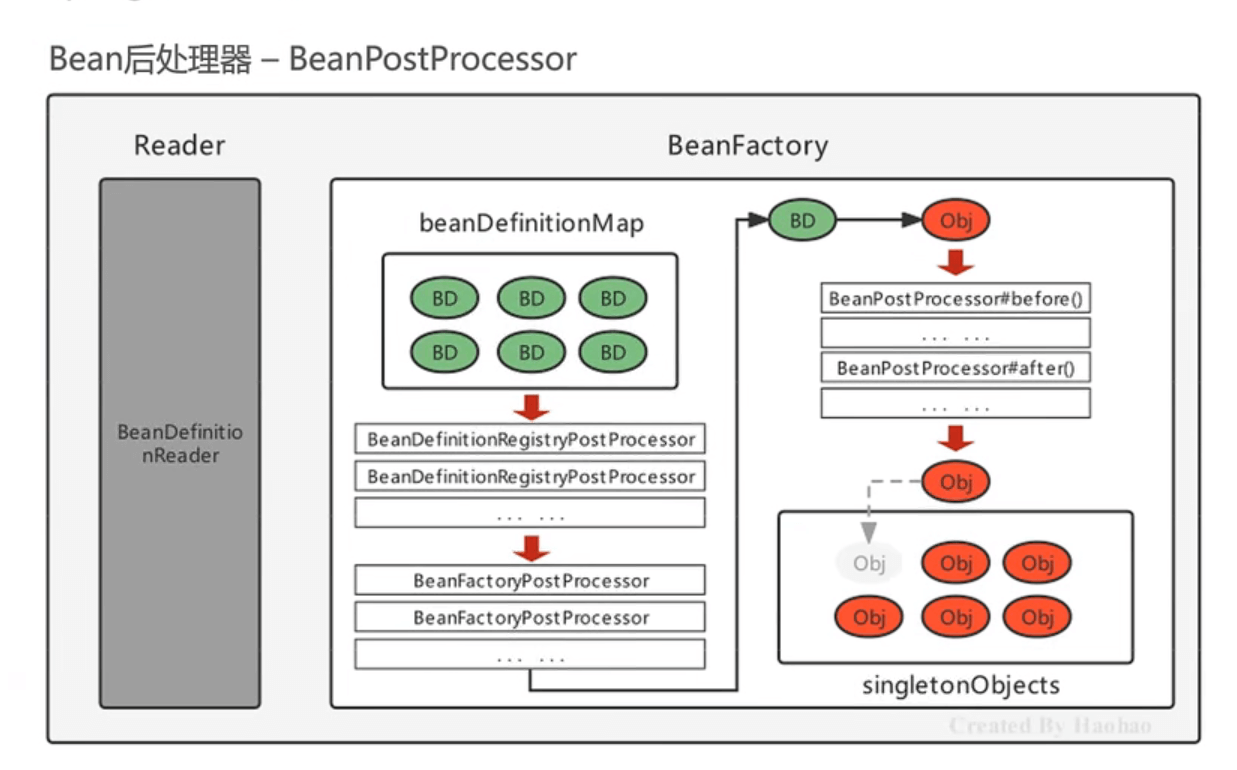
2.1 基本使用
BeanPostProcessor 源码如下,实现该接口可以实现两个方法,但不是必须的。
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}2.2 相关方法执行顺序
现有如下对象 UserServiceImpl.java:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService, InitializingBean {
private String name;
private UserMapper userMapper;
public UserServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("UserService实例化-无参构造");
}
public UserServiceImpl(String name) {
System.out.println("UserService实例化-有参构造");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setUserMapper(UserMapper userMapper) {
System.out.println("依赖注入userMapper");
this.userMapper = userMapper;
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("执行初始化 init 方法");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("属性设置之后执行初始化 afterPropertiesSet 方法");
}
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("show....");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}则执行方法的顺序如下:
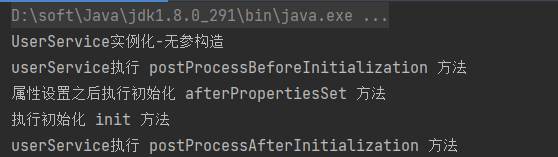
2.3 案例-实现日志增强
UserServiceImpl.java 同上,UserService.java 如下:
public interface UserService {
void show();
}必须定义一个接口,因为动态代理中生成的代理对象类型是根据目标对象实现的接口来确定的,不能直接强转为对象。
TimeLogBeanPostProcessor.java
public class TimeLogBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Nullable
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 使用动态代理对目标Bean进行增强,返回proxy对象
Object beanProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
((proxy, method, args) -> {
// 1. 输出开始时间
System.out.println("方法:" + method.getName() + "开始时间:" + new Date());
// 2. 执行目标方法
Object result = method.invoke(bean, args);
// 3. 输出结束时间
System.out.println("方法:" + method.getName() + "结束时间:" + new Date());
return result;
})
);
return beanProxy;
}
}xml 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.amjun.spring2.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" init-method="init">
</bean>
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.amjun.spring2.mapper.impl.UserMapperImpl">
</bean>
<!-- 测试 BeanPostProcessor -->
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.amjun.spring2.processor.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="timeLogBeanPostProcessor" class="com.amjun.spring2.processor.TimeLogBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
</beans>测试:
public class ApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans2.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.show();
}
}结果如下:
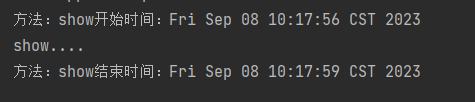
三、完整流程图
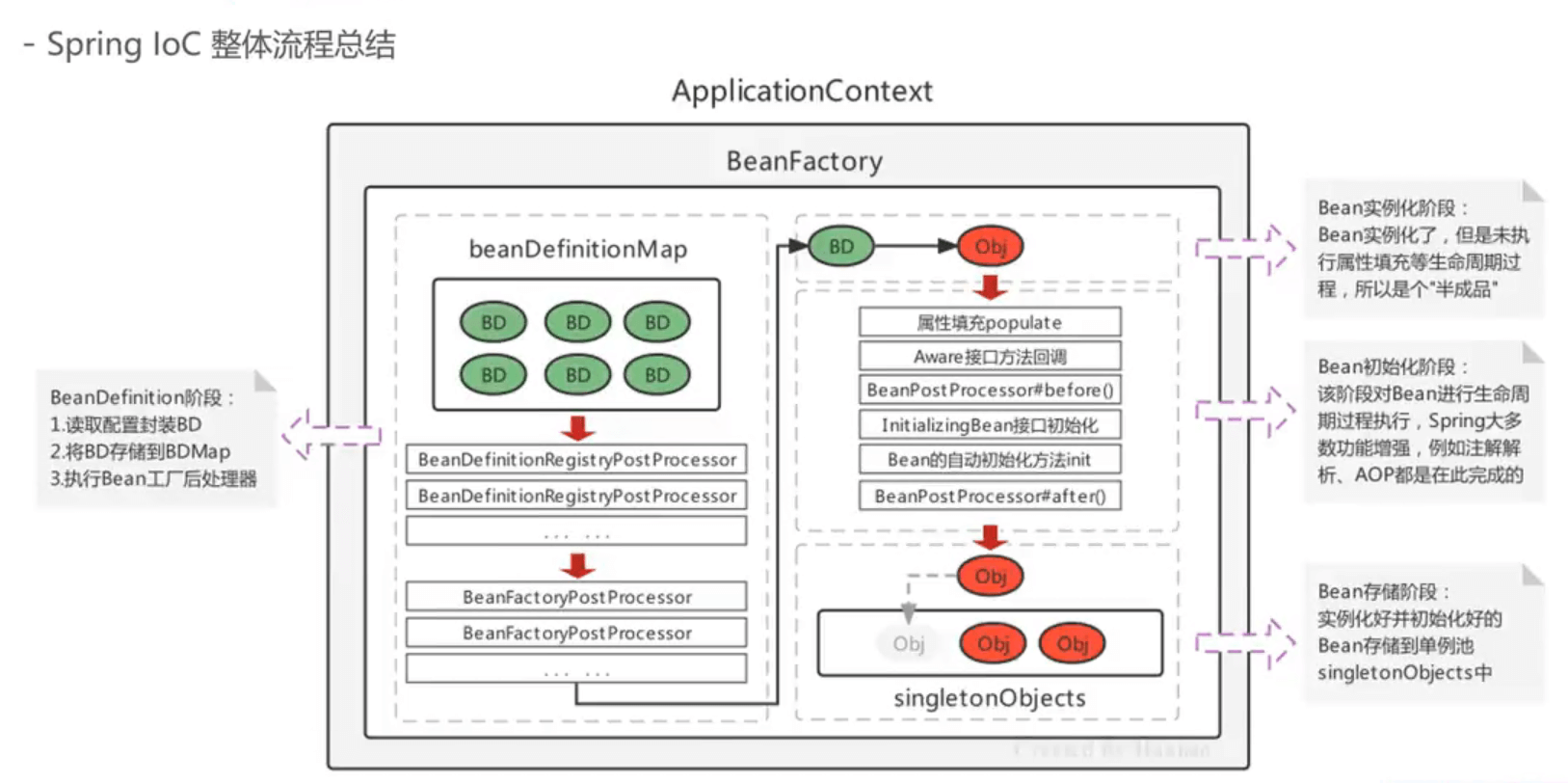
此流程图基于上诉流程图演变,且 bean 初始化阶段除了 Aware 接口方法回调基本都接触过。
这里简单了解一下 Aware 接口, 它允许 Bean 在被 Spring 容器创建时获取对容器或其他相关对象的引用,以便进行进一步的自定义操作或获取特定的资源。
以下是几个常见的Aware接口及其作用:
-
ApplicationContextAware:实现该接口的Bean可以获取对ApplicationContext的引用,从而可以在运行时访问Spring容器的功能和资源。
-
BeanFactoryAware:实现该接口的Bean可以获取对BeanFactory的引用,以便在需要时访问BeanFactory的功能。
-
BeanNameAware:实现该接口的Bean可以获取其在Spring容器中注册的名称。
-
EnvironmentAware:实现该接口的Bean可以获取对Environment的引用,以便在运行时获取配置属性和环境变量。
-
ResourceLoaderAware:实现该接口的Bean可以获取对ResourceLoader的引用,以便在运行时加载外部资源。
举个例子。
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware {
private String name;
private UserMapper userMapper;
public UserServiceImpl() {
//System.out.println("UserService实例化");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setUserMapper(UserMapper userMapper) {
//System.out.println("userService注入userMapper");
this.userMapper = userMapper;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("创建userService的BeanFactory: " + beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println("userService的beanName: " + beanName);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("创建userService的ApplicationContext: " + applicationContext);
}
}ApplicationContextTest.java
public class ApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans3.xml");
UserServiceImpl userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserServiceImpl.class);
System.out.println(userService);
}
}结果如下:

打印的这些内容都是创建对象之前无法获取的,因为 beanName 是在 xml 配置文件中指定的,ApplicationContext 获取到的 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 也是在测试时创建的。
提醒:本文发布于849天前,文中所关联的信息可能已发生改变,请知悉!







